Urgent and radical change is needed to address the declining dental health of Aotearoa’s children, but the problem is too huge to be tackled by just one service, a group of oral specialists say.
A paper published in the Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand, led by University of Otago pediatric dentistry senior lecturer Dr. Dorothy Boyd, says dental decay is the most prevalent non-communicable childhood disease in New Zealand. Māori, Pasifika, those from low socio-economic backgrounds, and those without access to community water fluoridation are most affected.
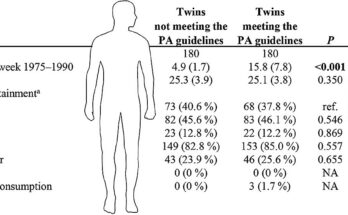
Aotearoa has a long tradition of providing publicly funded dental care for children and young people, yet by age 5, 60% of Māori, 70% of Pasifika, and 33% of non-Māori/non Pasifika children have already experienced dental decay, Dr. Boyd says.
“Early childhood caries—disease in young children’s teeth—has been described as a modern neglected epidemic and is getting worse.
“Despite the hard work of dental professionals in the midst of the early childhood caries tsunami, every part of the oral health care system is stressed, with long waiting lists, inconsistent collaboration between primary, secondary and tertiary care, and inconsistent access to, and types of, care offered across the country.”
This all compounds the suffering of children and whānau, she says.
“The entire oral healthcare workforce is under-resourced, and Māori and Pasifika are under-represented in it.”
The problem is too far-reaching to be managed without a collaborative and coordinated approach across health and society as a whole, Dr. Boyd says.
“Now is an opportunity for radical change, and that radical change is essential. However, for oral health to improve this cannot be left to oral health services—the problem is too huge, and overlaps with many other health needs. So, as a society it is time for us to demand that our children are protected from harm and enabled to be healthy.
“As a nation, we cannot afford not to invest in the health of our children.”
Preventing dental caries requires buy‑in from society, government, industry, health professionals and the public to understand and support a shift of focus away from getting fillings to placing value on children saying caries-free.
Reducing the extent of unhealthy foods marketed to children and addressing the affordability of healthy food, fluoride toothpaste and toothbrushes, is a good start, she says.
Living in deprivation has consequences for the health of children that follow them into adulthood; for example, most Pasifika adults only access dental care because of pain, and the cost is the main reason for not accessing routine dental care.
The solution lies in sustained, streamlined activity across the whole of society and particularly among services that care for children in health and beyond, she says.
“All children deserve to eat, sleep, learn and play without dental pain and oral infection.
“We all must agitate for changes that will enable children to grow up in Aotearoa New Zealand with the health that they deserve.”
Dorothy H. Boyd et al, Oral health of children in Aotearoa New Zealand–time for change, Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand (2022). DOI: 10.1080/03036758.2022.2069826
Citation:
Dental system failing children, urgent change needed according to oral specialists (2022, July 6)
retrieved 9 July 2022
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2022-07-dental-children-urgent-oral-specialists.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Source link